Corporate Finance - Introduction
Objective of Corporate finance is to maximize the value for shareholders.
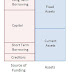
Sources of Money
a) Spontaneous source of money: Some part of money is possible to raise from supplier (called creditors).
b) Non-spontaneous source of money: Debt and equity.
From the corporate perspective, debt is relatively cheaper compared to money raised from equity. Interest are paid for debt whereas dividend are paid for money raised from equity. Interest paid for debt is chargeable before tax in profit and loss account, and so company pay less tax. Debt is risker than equity from corporate perspective as equity holder get dividend only based on the performance of firm whereas debt holders get fixed amount.
From the corporate perspective, debt is relatively cheaper compared to money raised from equity. Interest are paid for debt whereas dividend are paid for money raised from equity. Interest paid for debt is chargeable before tax in profit and loss account, and so company pay less tax. Debt is risker than equity from corporate perspective as equity holder get dividend only based on the performance of firm whereas debt holders get fixed amount.
Cost of debt is physical money going out.
Cost of equity is expectations of equity holder.

Assets
Fixed assets - land, building, machinery. Property of any fixed asset -> it last longer
Current assets - raw material, receivables, Propery of any current asset -> it last for short period. get convert into finished goods.
Role of Finance
The role of an accountant is to take measurements of a company's health and writes reports. Financial Manager examines the data prepared by accountants and make recommendations to top management regarding strategies for improving the company's financial strength.
Decision making in corporate finance:
1. Capital investment decision (Fixed asset)
2. Capital structure decision (long term borrowing, capitals)
3. Working capital management (current liability, current assets)
4. Dividend payouts
Financial Markets
1. Capital market -> Item in long-term in nature -> Equity and Debunture are example instruments
2. Money market -> Short term in nature ->
3. Bank market -> term loan
4. Forex market -> Don't raise any money but just change currency
Risk Managements
1. Insurance
2. Derivatives -> Financials, Commodity
Regulators in India
FM -> 1. SEBI
RM -> 2.3.4 -> RBI
RM 1 -> IRDA
RM 2 -> Finaicals -> SEBI,
RM 2-> Commodity -> FMC
Corporate Finance - Introduction
 Reviewed by Sourabh Soni
on
Sunday, March 03, 2013
Rating:
Reviewed by Sourabh Soni
on
Sunday, March 03, 2013
Rating:
 Reviewed by Sourabh Soni
on
Sunday, March 03, 2013
Rating:
Reviewed by Sourabh Soni
on
Sunday, March 03, 2013
Rating:

![Katraj To Sinhgad Trek [Interactive Route]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEg9ZnVgkd3y54CNcPghhExIFAGwxo53QsQz12goWNjQ-S9VO_7eJ_mCCC_d10IRcCfKyXZqn-Jlznp1JWxjrQijmG3kskJe-RjV_xOo10z7vUjt4lninVk-kjJeKdJFVFtHVRL7iki0aaW6/s72-c/IMAG0342.jpg)





Thanks for picking out the time to discuss this, I feel great about it and love studying more on this topic. It is extremely helpful for me. Thanks for such a valuable help again. buy-now-pay-later-desktop-computers
ReplyDelete