Introduction to Balance Sheet
Financial statements are summary of accounting transactions & are presented in a manner to enable users know the operating performance of the organization and also its impact on the overall value of the organization.
Balance sheet is the one of the most important financial statement that reports financial position on a particular day. It is a cumulative report of a company’s assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity. The balance sheet reflects the accrual based accounting to match the revenues and associated the expenses.
It shows the equality of assets and liabilities plus net worth
Assets = Liabilities + Owner's equity
Norms of Financial Accounting
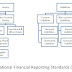
Different accounting standards suggest different set of accounting practices. International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) are designed as a common global language for business accounting across international boundaries. Indian Accounting Standards (IAS) is accounting standards followed in India. These norms of accounting gives the classification of assets & liabilities, and defines the format of the financial statements. Following two pictures depict the classification of assets in liabilities under IFRS and Indian generally accepted accounting practices (GAAP).
Terms in Balance Sheet
Current assets are assets that will turn into cash within one year of an operating cycle. They are listed in order of how they are easily converted into cash or liquidity, cash being the most liquid. It includes
Intangible assets refers to non-monetary assets that have no physical substance and will last more than 1 year. These include patents, copyrights, trademarks, and rights.
Though goodwill is a intangible asset, it is listed on its own and separate from the list of intangible assets.
Current liabilities need to be paid within one year of an operating cycle. Current liabilities include following:
- Cash and cash equivalent
- Marketable securities (stocks, bonds, etc.)
- Accounts receivable or sundry debtors
- Supplies
- Inventory
- Prepaid expenses (prepaid insurance, prepaid rent, etc.)
Fixed assets are investment of a company in it's own business i.e. plant, building etc. that helps in operating the business. Fixed assets are also referred as long-term assets. It is calculated as a company's value of property, plant, and equipment that can be used for more than one year, minus depreciation. Fixed assets are further classified into tangible and intangible assets.
Intangible assets refers to non-monetary assets that have no physical substance and will last more than 1 year. These include patents, copyrights, trademarks, and rights.
Though goodwill is a intangible asset, it is listed on its own and separate from the list of intangible assets.
Current liabilities need to be paid within one year of an operating cycle. Current liabilities include following:
- Accounts payable or creditors
- Short-term notes payable
- Taxes payable
- Wages payable
- Unearned revenues
- Long-term notes and mortgages
- Bonds payable
- Pension plan obligations
Net income earned by the firm in an operating cycle is divided into two parts viz. dividend (to the stockholders) & retained earnings. Retained earnings is the amount that remained with the firm after distributing the dividend. This amount is carried forward in the balance sheet. Reserved & surplus is same as retained earnings
Capital employed is owner's fund plus loaned fund (debt or contributed capital)
Introduction to Balance Sheet
 Reviewed by Sourabh Soni
on
Thursday, March 14, 2013
Rating:
Reviewed by Sourabh Soni
on
Thursday, March 14, 2013
Rating:
 Reviewed by Sourabh Soni
on
Thursday, March 14, 2013
Rating:
Reviewed by Sourabh Soni
on
Thursday, March 14, 2013
Rating:





![Katraj To Sinhgad Trek [Interactive Route]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEg9ZnVgkd3y54CNcPghhExIFAGwxo53QsQz12goWNjQ-S9VO_7eJ_mCCC_d10IRcCfKyXZqn-Jlznp1JWxjrQijmG3kskJe-RjV_xOo10z7vUjt4lninVk-kjJeKdJFVFtHVRL7iki0aaW6/s72-c/IMAG0342.jpg)



No comments