Elasticity of Demand or Supply
Elasticity of demand
The price elasticity of demand is indicates how sensitive is the demand quantity to the change in price. It is the ratio of the percentage change in quantity to the percentage change in price. In general, elasticity of demand can also be calculated in terms of other demand factors like income of consumer.
The elasticity of demand for q with respect to demand factor y is defined as the percentage change in q as a result of 1 % change in y. Here the y could be any parameter that affect the demand e.g. income
The very flat demand curve indicates that a small change in price has a large effect on the demanded quantity. Likewise, very steep demand curve indicates that even a large change in price does not effect on the quatity demanded too much.
Point elasticity: When the elasticity is measured based on the percentage change relative to the value of taken at the variable point, the elasticity is called point elasticity. e.g. y -> y1 and q -> q1
Arc elasticity is the elasticity that is measured based on percentage changes relative to the average value of each variable between two points. y = (y1 + y2)/2 & q = (q1 + q2)/2
Price Elasticities Along a Linear Demand Curve
For a straight line demand curve, the price elasticity of demand varies between different pairs of points along the curve.
The lower the price and the greater the quantity demanded and so the lower the absolute value of the price elasticity of demand. At mid-point on the demand curve, the price elasticity of demand has value 1 and it is termed as unit-elastic demand. And at the points above mid point, its has value greater than 1 and this is termed as elastic demand. Whereas at the points below mid-point, it has value less than 1 and it is termed as inelastic demand
The price elasticity of demand at point 'X' on the curve,
e = Q2X / P0X
The lower the price and the greater the quantity demanded and so the lower the absolute value of the price elasticity of demand. At mid-point on the demand curve, the price elasticity of demand has value 1 and it is termed as unit-elastic demand. And at the points above mid point, its has value greater than 1 and this is termed as elastic demand. Whereas at the points below mid-point, it has value less than 1 and it is termed as inelastic demand
Constant Price Elasticity of Demand Curves
1 . Perfectly elastic demand means that the change in quantity is infinite for very tiny change in price; the demand curve in this case is horizontal. Elasticity is infinity.
2. Perfectly inelastic demand means that the change in quantity is zero for any percentage change in price; the demand curve in this case is vertical. Elasticity is zero.
3. Iso elastic -> same elasticity at all points -> q = y^-a.
Range of Price Elasticity of Demand Curves
Range of Price Elasticity of Demand Curves
It ranges from 0 to + infinity.
e = 0 => Perfectly inelastic
0 < e < 1 => Inelastic
e = 1 => Unit elasticity
e > 1 => Elastic
e = + infinity => Perfectly elastic
Price Elasticity of Demand and Changes in Total Revenue
Total revenue is the price of the sold good or service multiplied by the number of units of sold quantity.
If the price elasticity of demand is elastic (i.e. > 1), then the increase in price would reduce the TR whereas the reduction in price would increase the total revenue.
If the price elasticity of demand is inelastic (i.e. e < 1), then the increase in price would increase the TR and the reduction in price would decrease the total revenue.
Income Elasticity of Demand
em < 0 (i.e. -ive) for inferior goods
em > 0 (i.e. +ive) for normal goods
0 < em < 1 -> Necessity
em > 1 -> Luxury
Cross-price Elasticity of Demand
exy < 0 (i.e. -ive) for complements (e.g. tea & sugar)
exy > 0 (i.e. +ive) for substitutes (e.g. tea & coffee, or coke & pepsi)
Elasticity of Demand or Supply
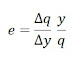 Reviewed by Sourabh Soni
on
Sunday, December 09, 2012
Rating:
Reviewed by Sourabh Soni
on
Sunday, December 09, 2012
Rating:
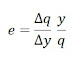 Reviewed by Sourabh Soni
on
Sunday, December 09, 2012
Rating:
Reviewed by Sourabh Soni
on
Sunday, December 09, 2012
Rating:






![Katraj To Sinhgad Trek [Interactive Route]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEg9ZnVgkd3y54CNcPghhExIFAGwxo53QsQz12goWNjQ-S9VO_7eJ_mCCC_d10IRcCfKyXZqn-Jlznp1JWxjrQijmG3kskJe-RjV_xOo10z7vUjt4lninVk-kjJeKdJFVFtHVRL7iki0aaW6/s72-c/IMAG0342.jpg)



Good. You may find following link interesting:
ReplyDeletehttp://catalog.flatworldknowledge.com/bookhub/reader/21?e=rittenberg-ch05#rittenberg-ch05_s02