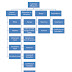
Summary Measures
Summary measures in descriptive statistics are used to summarize a set of observations, commonly, in following ways
- Measures of central tendency like mean, median, mode, geometric mean, harmonic mean
- Measures of dispersion like range, variance, standard deviation
- Measures of the shape of the distribution like skewness or kurtosis
- Measures of dependence like correlation coefficient
Measures the tendency of data values to group around a central value.
- Mean, commonly known as average, is the sum of all values divided by the number of cases. This is also known as arithmetic mean.
- Mode is the most frequent value in a data distribution. The mode is suitable for all types of data (nominal to ratio data). In practice, the mode is suitable only for variables with limited values
- Median is the value that exactly divides an ordered set of data into equal halves. If the size of ordered data is odd number then middle number will be median whereas if its even number then average of middle two numbers gives the median. The median is not affected by extreme values. The median is suitable for ordinal data and cannot be used for nominal data
- Geometric mean is nth-root of product of all values in data-set. The geometric mean is suitable for ratio data. This more appropriate than arithmetic mean of proportional growth e.g. CAGR.
- Harmonic mean is calculated by taking the reciprocal of average of reciprocal of data. Harmonic mean is appropriate for calculating the average of rates. Unlike arithmetic mean which gives greater weightage to large data points than to small data points, harmonic mean gives equal weightage to all data points.
Measures the spread or dispersion of values in a data set.
- Range is the difference of largest value and smallest value in the data set. It measures the total spread in the set of data.
- Inter Quartile Range IQR (mid-range) is the difference between values at the 25th and the 75th percentiles in the data set. This is more stable than the range but is of limited use.
- Sum of squares is the sum of the squared deviations of set of data from the mean of the set. This is also known as Variation.
- Variance is the mean of the squared deviations.
- Standard deviation is the square root of the variance. This is a most commonly used measure of dispersion.
- Coefficient of variation expresses the standard deviation in percentage of mean.
- Z-Score is the difference between the value and the mean, divided by the standard deviation. This is used to locate the outliers in the data-set. The larger the Z-score the greate the distance from the mean.
Measures of Shape
Measures the shape or pattern of distribution of data values through out the range.
- Uni-modal - the distribution had only a single value that occurred most frequently
- Symmetrical - the left side of the distribution of values mirrored the right side
- Skewed - when left side and right-side of distribution does not mirror each other. It can be skewed to the left or skewed to the right
- Bell-shaped - the frequencies of cases declined toward the extreme values in the right and left tails, so that the distribution had the appearance of a "bell".
It can be symmetric or skewed distribution around the mean value of data set.
- Skewness measures the extent to which a set of data is not symmetric.
- Kurtosis measures the relative concentration of values in the center of distribution. It measures the peakness of the distribution
Measures of dependence
Measures the cause and effect relation among the variables.
- Covariance measures the strength of the linear relationship between two numerical variables
- Coefficient of correlation measures the relative strength of the linear relationship between two numerical variables
Summary Measures
 Reviewed by Sourabh Soni
on
Sunday, December 02, 2012
Rating:
Reviewed by Sourabh Soni
on
Sunday, December 02, 2012
Rating:
 Reviewed by Sourabh Soni
on
Sunday, December 02, 2012
Rating:
Reviewed by Sourabh Soni
on
Sunday, December 02, 2012
Rating:










No comments